
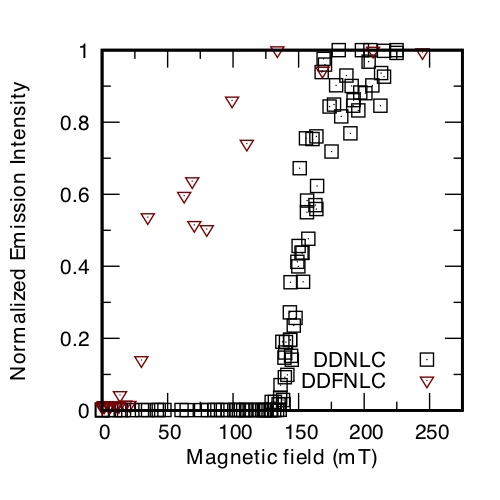
Random laser action, resulting from the multiple scattering of light, can be observed in dye-doped nematic liquid crystals (NLCs). The intensity of random laser emission can be controlled by electric, thermal and magnetic stimuli, however, the magnetic control needs very strong magnetic field because the magnetic anisotropy of LC molecule is low. Recently, ferromagnetic NLCs (FNLCs) was reported; ferromagnetic nanoplatelets (MNPs) dispersed in an NLC are oriented in the same direction as the nematic director, which can be reoriented by very weak magnetic field by virtue of the ferromagnetism. Here, we report magnetic-field-induced change of the random laser action in dye-doped FNLC (DDFNLC). Dye-doped NLCs (DDNLCs) were prepared by doping nematic liquid crystal, E7, with 0.3 wt% of Pyrromethene 597 as a laser dye. A suspension of 0.6 wt% MNPs in 1-buthanol was mixed with DDNLCs. The mixture was kept at 70 °C for 24h to evaporate 1-buthanol to give DDFNLCs with 0.1 wt% of MNPs. DDNLCs and DDFNLCs were injected into homeotropic alignment cells. The samples were optically pumped by pulsed laser at 532 nm and the emission spectra were measured at different magnetic field intensities. Without any magnetic fields, no random laser action occurred. Laser action started from about 10 mT and 140 mT of magnetic fields parallel to the cell surface for DDFNLCs and DDNLCs, respectively (Figure). The random laser is likely to emit perpendicularly to the nematic director; in fact, in a magnetic field parallel to the cell surface, the nematic director in a homeotropic in an alignment cell rotates to the direction parallel to the cell surface and the random laser emission is switched on. Moreover, we can conclude that the addition of MNPs lowers the threshold magnetic field of the random laser action to about one tenth.
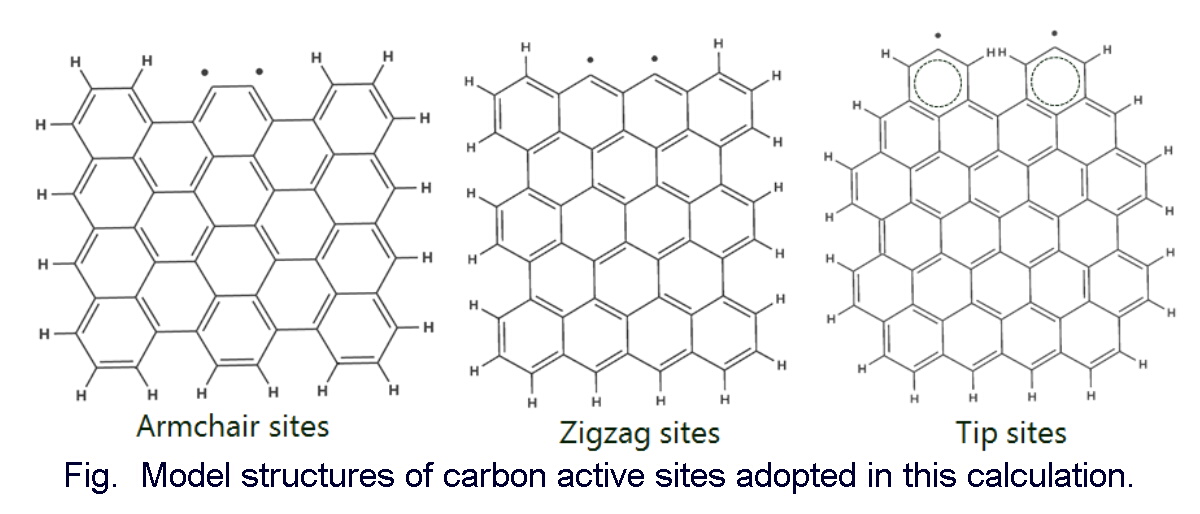
Studies on chloric behavior in high temperature processes (such as pulverized coal firing, waste burning and iron ore sintering) are important because volatile noxious compounds can be generated. For example, when heating coal to achieve burning and gasification, pyrolysis occurs first, volatile components are released and chlorine in coal is reported to be desorbed as HCl in this process. In addition, HCl is generated by the incineration of waste and then reacted to generate dioxins and chlorinated benzene. For blast furnace pig iron, some chlorine is captured into the solid-phase coke during the process of exhaust gas treatment at low temperatures. Our research group has previously studied the adsorption of HCl by Zn-doped O2-activated resins at 100 and 300 °C. It was clarified that a Zn-doped carbon compound adsorbs HCl much more than a carbon compound at 100 and 300 °C. However, the kind of reaction site and influence of metal on carbon active site have not been clarified with respect to the metal-doped carbon active site and the adsorption stability of HCl. Also, no research has focused on this point. In this study, electronic states of three carbon active site models (Armchair, Zigzag and Tip sites) before and after Zn doping were calculated by molecular orbital calculation (RHF/6-31G*). Calculation results of molecular orbital method for molecular models of carbon and Zn-doped carbon materials suggested that the presence of Zn may increase the number of chemisorbed sites for HCl molecules. In addition, it was estimated that ZnO does not contribute to the adsorption stability of HCl on the Zigzag sites. It has also been clarified that ZnO greatly affects the electronic state of the whole carbon material. In the future, this study makes it possible to propose a method to inhibit the generation of volatile hazardous compounds in high temperature processes.
Liquid crystalline (LC) elastomers are very promising functional materials providing unique properties by coupling of "dynamic property of polymer networks" and "anisotropy of LC phases (such as orientation order of LC molecules)" [1-3], and thereby these materials are applicable to artificial muscles and soft actuators in the field of a variety of robotics. In this study, we demonstrate the spherical LC elastomers responsive to an electric field as micro size actuators. In addition, the creation of the spherical LC elastomers containing dual frequency LCs of which the dielectric anisotropy can be controlled by the frequency of AC field was newly investigated by using a flow focusing device (Figure 1). Then, the influence of the amounts of the LC molecules and the crosslinkers in the precursors on the deformation amounts of the elastomers was also discussed at the given frequencies of the applied AC fields.
The phase transition behavior of the elastomers was identified by polarized optical microscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. The results revealed that the elastomers exhibited a LC phase below 60 °C.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Kyoto Technoscience Center and Murata Science Foundation.
References
1. T. Ikeda, J. Mamiya, Y. Yu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 506-528.
2. H. Yang, A. Buguin, J.-M. Taulemesse, K. Kaneko, S. Méry, A. Bergeret, P. Keller, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 15000-15004.
3. K. Urayama, E. Kohmon, M. Kojima, T. Takigawa, Macromolecules, 2009, 42, 4084-4089.

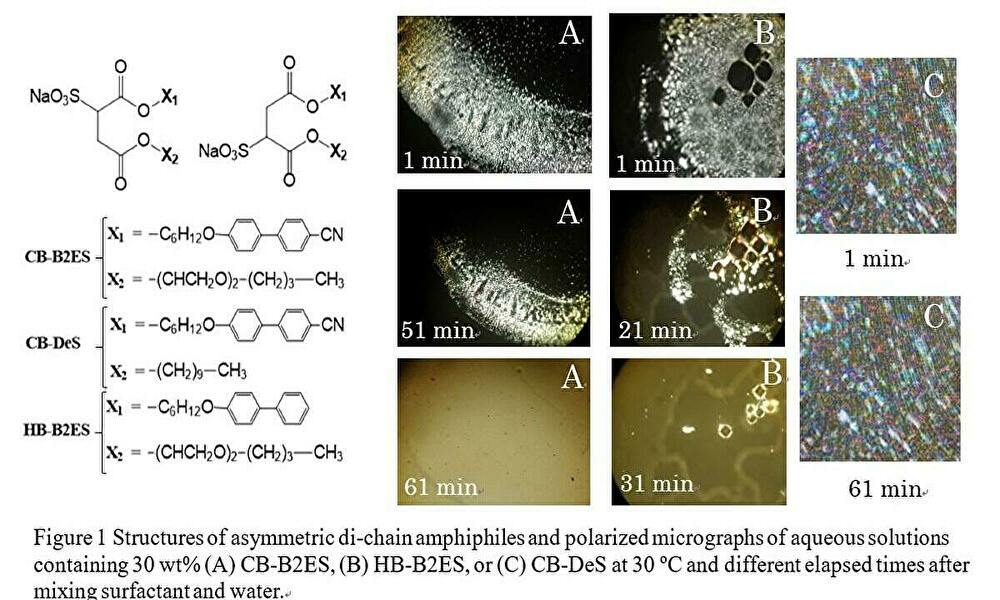
Amphiphiles having different hydrophobic chains (such as fluorocarbons and hydrocarbon chains) often exhibit unusual interface properties and liquid crystal behavior. To generate a new drug release function of liquid crystals, this study synthesized amphiphiles having oxyethylene units and thermotropic liquid crystal mesogens (i.e. cyanobiphenyl and biphenyl groups) in the hydrophobic two chains (CB-B2ES and HB-B2ES, respectively) and a CB-B2ES analogue without oxyethylene units (CB-DeS). Then lyotropic liquid crystal behavior of the amphiphiles in water was investigated as functions of temperature and elapsed time. Figure 1 shows chemical structures of amphiphiles and polarized micrographs for 30 wt% amphiphile / water mixtures at 30 °C at different elapsed times after preparation. Mixtures containing CB-DeS, CB-B2ES and HB-B2ES displayed maltese cross textures, suggesting formation of a lamellar liquid crystal. Lamellar liquid crystals in the CB-DeS / water mixture were stable and showed no morphology change without applying external forces or change in experimental condition. However, in CB-B2ES and HB-B2ES / water mixtures, lamellar aggregates displayed dynamic formation/breakdown behavior with elapsing time at a constant temperature. Namely, after preparation of fresh mixtures, population of maltese cross textures gradually increased but suddenly all the textures disappeared in a few min. The time to start the maltese texture breakdown for CB-B2ES was ~30 min at 30 °C, longer than that for HB-B2ES. It probably results from the higher stability of CB-B2ES lamellar LCs by additional electrostatic interaction between cyanobiphenyl groups. In addition, there were no change in 1H-NMR spectra before and after the texture breakdown. It suggested that the texture breakdown was not caused by decomposition of the surfactants. The dynamic liquid crystal behavior of the texture breakdown was expected to happen by phase transition from lamellar to another isotropic phase with elapsing time.
Clathrate hydrate of tetra-n-butylammonium bromide (TBAB) is expected as a cold storage material for air conditioning, but supercooling is a problem for practical use. The supercooling, widely known, is the state of maintaining the liquid phase even if it is cooled below freezing point, but the detailed mechanism is not clarified. For the purpose of visualization of the supercooling phenomenon, both the structures of TBAB clathrate hydrate and TBAB aqueous solution were observed. In general, although scanning electron microscope (SEM) is widely used in the observation of micro- or nano-size objects, it had not been possible to observe such as a solution or a gel directly since the inside of the SEM is under a high vacuum. Therefore, SEM observation was performed by a freeze fracture replica method. Freeze fracture replica method is utilized not only in medicine and biology fields but also in various fields since it is possible to obtain both of the information of a solution itself and the state of particles having a microstructure simultaneously. Specifically, cut-surface of the quenched sample was prepared and thin film is fabricated on the cut-surface. And by soaking it in an appropriate solvent, the thin film and the sample were separated to recover a replica film reflecting the morphology of quenched cut-surface. Finally, the replica film was observed by SEM.
In this study, we tried to observe the solution structure in the process of crystallization and melting of TBAB supercooled aqueous solution. Further, in actual use of a cold storage material, a hysteresis phenomenon (called a memory effect) accompanying a thermal history often becomes a problem. The memory effect was also investigated in relation to the solution structure by another analysis methods other than the freeze fracture replica method. The characteristics of the memory effect were clarified according to various analysis methods. We are going to discuss the results.
Here, we investigated the phase equilibria of the methane hydrate containing organic inhibitors (methanol; MeOH and ethylene glycol; MEG) and ammonuium chloride (NH4Cl). Conventional isochoric trace method to identify the equilibrium temperatures and pressures for methane hydrates with mixed inhibitor system was used, and two groups of mixed inhibitor solutions: (1) 5 wt% NH4Cl + 10 wt% MEG, 5 wt% NH4Cl + 20 wt% MEG, 10 wt% NH4Cl + 10 wt% MEG, 10 wt% NH4Cl + 20 wt% MEG aqueous solutions, and (2) 5 wt% NH4Cl + 10 wt% MeOH, 5 wt% NH4Cl + 20 wt% MeOH, 10 wt% NH4Cl + 10 wt% MeOH, and 10 wt% NH4Cl + 20 wt% MeOH aqueous solutions, were prepared. The phase equilibrium conditions of methane hydrates containing MEG/MeOH and NH4Cl solutions are located at lower temperature and higher pressure conditions than those of pure methane hydrate. In addition, as the concentration of MEG/MeOH and NH4Cl increase, the hydrate equilibrium conditions of methane hydrates are further shifted into left regions (lower temperature and higher pressure conditions). The hydrate inhibition performance of our mixed inhibitor system is in the following order; (10 wt% NH4Cl + 20 wt% MeOH/MEG) > (5 wt% NH4Cl + 20 wt% MeOH/MEG) > (10 wt% NH4Cl + 10 wt% MeOH/MEG) > (5 wt% NH4Cl + 10 wt% MeOH/MEG). After all, we calculated the dissociation enthalpies of methane hydrates containing mixed inhibitor solutions using the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, which fits well with the experimental data.
KEYWORDS : methane hydrate, phase equilibria, thermodynamic hydrate inhibitor, ammonium chloride
Methane hydrates vastly deposit in deep sea around Japan, and expected as one of unconventional natural gas resources. The depressurization method is being developed for methane gas production from subsea methane hydrates. Methane hydrates are only stable at high pressure and low temperature conditions. In the depressurization method, a pipe equipped with depressurization pump is inserted into the subsea methane hydrate layer. When the methane hydrate layer is depressurized by the pump, the methane hydrates dissociate to gas and water. When the well pressure returned to be seawater head pressure by an accident or during operation stop, the methane hydrates may reform and plug the flow channel in the well. As a solution to dissociate the hydrate blockage, injection of a thermodynamic hydrate inhibitor (THI) into the well is effective, because the THI can melt the methane hydrates by shifting equilibrium curve toward lower temperature, in other words, freezing point depression. In this study, as a part of a Japanese National hydrate research program (MH21, funded by METI), we demonstrate methane hydrate dissociation by injection of urea which is expected for environmentally-friendly THI. In combination with urea, we used kinetic hydrate inhibitors (KHIs) or promoters such as polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). The experiments were carried out in the rocking cell equipped with three glass windows. The cell was rocked to facilitate mixing of the fluids and solids inside the cell. Methane hydrates were first formed at 13 MPa and 278 K in the cell. A THI solution was stepwise injected into the cell to dissociate the hydrates. The dissociation behavior was recorded by a CCD camera. We tested a couple of different solutions of THI and the kinetic inhibitors/promoters. The present results suggest that there is a synergetic effect on the hydrate dissociation by combinations of urea and inhibitors/promoters.
Separation and recovery technologies for carbon dioxide (CO2) are needed to address global warming. Semi-clathrate hydrates (SCH) with tetra-n-butyl ammonium bromide (TBAB) are attractive as CO2 separation media, because they can be simply regenerated and reused. Although SCH as slurries can possibly be applied to continuous separation processes, the reasons for their rheological properties being Bingham fluid or pseudo-plastic fluids are unknown and are important for their practical application. In this work, the objective was to investigate the relationship between the SCH crystal morphology and flow characteristics of SCH hydrate slurries so that the fundamental basis for their rheological properties can be understood. The shape of SCH crystals in the slurries was changed by time maintained super-cooling after crystal formation, defined as the overcooling time. Initial TBAB concentration was 10.4 wt% in the TBAB aqueous solution before the hydrate slurry formation and experimental temperature was 278.5 K. The solid fraction (v/v) in the slurry was 0.12. The viscosities of the SCH slurries were measured with a rotational viscometer and results were analyzed with Herschel-Bulkley's model. Least-squares and mathematical optimization were used to determine viscosity index, fluid consistency coefficient and yield shear stress. Size and shape of SCH crystals were characterized with microscopy and particles were found to be needle-like and granular without overcooling time, and were only granular with an overcooling time of 30 min. The fluid behavior of the SCH slurry was only Bingham fluid with an overcooling time of 30 min. Therefore, the shape of the SCH crystals in the slurry was found to influence the rheological behavior of the slurries and their flow characteristics.
Biogas is a resource that has been proposed to provide carbon neutral energy and reduce CO2 emissions. However, biogas typically contains numerous impurities such as carbon dioxide, water and hydrogen sulfide, and these impurities must be removed before processing the mixtures with present technologies. Semi-clathrate hydrates (SCH) are attractive as gas separation media in biogas systems, because they are unaffected the presence of most impurities, however, there are issues related to their theoretical loading (adsorption amount). For tetra-n-butyl ammonium bromide (TBAB) semi-clathrate hydrates, it has been reported that CO2 absorption amount was much lower than theoretical values at TBAB concentrations above 1.5 mol%. The hypothesis explored in this work is that CO2 is not sufficiently absorbed in SCH slurries due to SCH crystal aggregation. The objective of this work was to investigate how to increase CO2 absorption amount in TBAB SCH slurries through experiments with a bubble column reactor. SCH slurries were loaded in the column, and gas mixtures were flowed through a filter from the bottom of the column. Loaded TBAB concentration was 0.55 mol%, experimental temperature was 278.2 K and experimental pressure was 0.8 MPa. Gas mixtures of He and CO2 were used in which initial CO2 composition was 0.20. The CO2 absorption amount was 1.86 mmol-CO2/mol-H2O. Occupancy of CO2 in SCH estimated from this result was 0.04. However, theoretical CO2 occupancy with a thermodynamic model was estimated to be 0.13, which indicates that the CO2 was not sufficiently absorbed by the SCH. The amount of hydrate in the slurry increased gradually as CO2 was absorbed into the slurry and CO2 tended to be enclathrated mainly in the inner cages of initial SCH particles. Thus, SCH formation in the initial stages of gas absorption is important for increasing the amount of gas absorbed into the slurry.
Natural gas is a growing energy source due to the less emission of carbon dioxide than other fossil fuels such as coal and oil. Various materials and methods have been investigated so far for effective separation, transportation, and storage. Among the options, gas hydrate has recently been received great attention due to its theoretically promising storage capacity and separation function. To evaluate the potential of gas hydrate as natural gas storage media, however, the fundamental thermodynamic properties should be fully investigated, particularly elucidating its distinct characteristics of cage occupation behavior of natural gas molecules. In this study, we investigated the binary gas hydrate containing trimethylene oxide (TMO) and CH4 molecules focusing on the distinct host-guest interactions between water cages (host) and guests (TMO and CH4). Pressure-temperature phase equilibria were measured. In addition spectroscopies such as synchrotron High Resolution Powder Diffraction (HRPD), Dispersive Raman, and 13C solid-state Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) were employed. The results indicated that the thermodynamic stability of TMO + CH4 hydrate was higher than that of pure CH4 hydrate. Particularly, structure II type gas hydrate was mainly formed at the concentrations of TMO below 5.56 mol%. When the ratio of water to TMO was 17: 1, abnormal tuning phenomenon was also observed. The cage occupancy of CH4 molecules in TMO + CH4 hydrate was significantly enhanced.
Light perovskite-type hydrides show great potential for hydrogen storage. Using density functional theory (DFT) modeling, all possible perovskite-type hydrides ABH3 (alkali metals A = Li, Na, K, Rb, or Cs, alkaline metals B = Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, or Ba) have been investigated to explore the structural stability and hydrogen release properties. The formation enthalpies and reaction enthalpies for hydrogen release were calculated based on the optimized experimental and hypothetical structures. The most favorable dehydrogenation pathways were obtained for all ABH3 systems studied. In addition, NaCaH3 was screened to be as one of the most promising material to store hydrogen among these perovskite-type hydrides. To facilitate the hydrogen release of NaCaH3, the dopants including alkali metals (Li, K, Rb, or Cs) and alkaline metals (Be, Mg, Sr, or Ba) were introduced to replace the Na and Ca sites in NaCaH3 structure, respectively. The reaction enthalpies of doped-systems were calculated by different dehydrogenation pathways. Among all dopants examined, the Cs was the most beneficial dopant for the dehydrogenation of NaCaH3 with the lowest energy required. However, there is no useful on hydrogen release using alkaline dopants in NaCaH3 system. Overall, for future experiment and theoretical work, these studies can provide valuable model to design new promising perovskite-type hydrides for hydrogen storage.
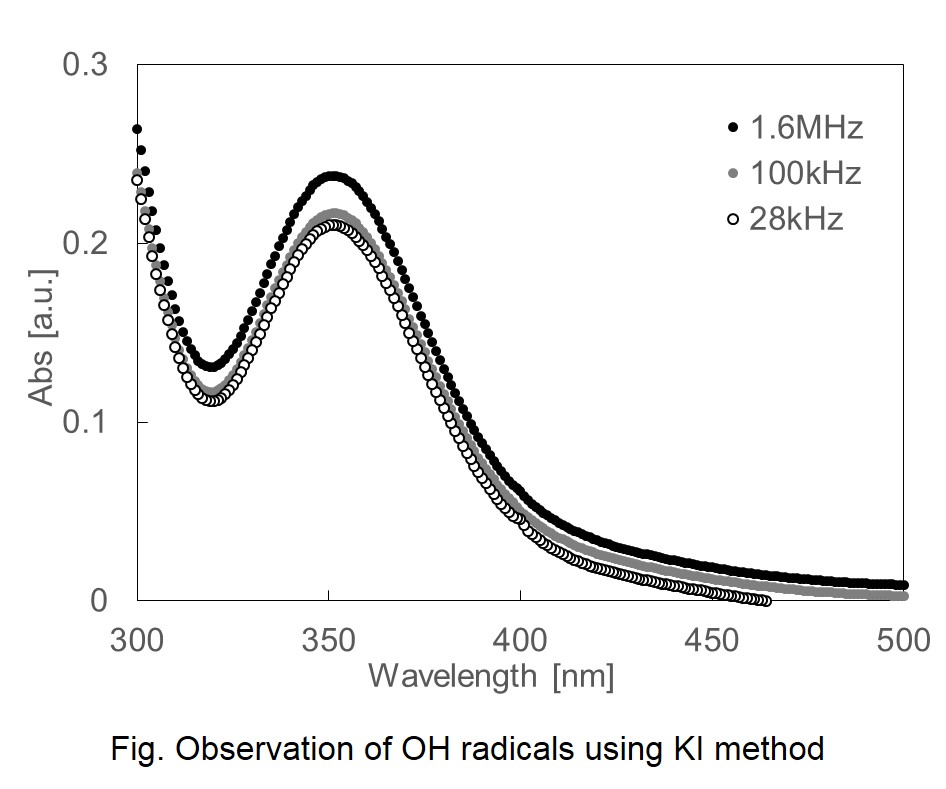
In this study, investigated the evaluation of ultrafine bubble (UFB) with diameters of 1 μm or less, which are important among fine bubble (micro / nano bubble) studies, using hydroxy (OH) radicals and sonoluminescence generated by the collapse of UFB when ultrasonic waves are applied to UFB. First, electron spin resonance (ESR) and potassium iodide (KI) techniques were used for the evaluation of OH radicals. From the measurement results of ESR, it was confirmed that OH radicals were generated by the collapse of UFB. Also, since the KI method stabilizes iodine dissociated from KI as I3- with an absorption wavelength of 355 nm when OH radicals are present, the generated OH radicals can be evaluated by measuring the absorbance of this I3- with a spectrophotometer. However, when air is used as an internal capsule gas, the observation of OH radicals generated by the collapse of UFB has been difficult to evaluate by the KI method because the difference in absorbance is very small. Therefore, distinct absorbance differences could be confirmed by increasing the amount of OH radicals generated by the collapse of UFB by using ozone as the inclusion gas. Furthermore, it was confirmed that the higher the frequency of ultrasound, the greater the difference in absorbance (Fig). On the other hand, sonoluminescence measurements confirmed the luminescence phenomenon with respect to UFB collapse by ultrasound, and further confirmed that the luminescence intensity of water with the addition of the same number of inorganic particles as UFB was smaller than that of UFB water. Since differences in experimental results were confirmed by the presence or absence of UFB in these multiple experiments, evaluation of UFB using OH radical as an index using ultrasound can be expected.
Friction is fundamental phenomena in various mechanical process. Therefore, better understanding of friction behavior from atomistic scale is significantly important. Conventionally, a flat metal surface has been used in the molecular dynamics for investigation of friction behavior. However, in the realistic system, a irregular morphology of the surface plays an important role for friction dynamics. Such surface modeler requires a lot of computational power in the molecular modeling, which becomes issue for application of molecular dynamics. In this paper, a novel molecular dynamics method will be presented for the modeling of friction behavior with less computational time.
Quartz is an important crystalline solid and its wettability plays an essential role in affecting various production processes. However, less attention has been paid to the crystal face related wetting behavior. In the present work, with the contact angle goniometer and the atomic force microscopy (AFM), the wettabilities of different faces of quartz were studied by measuring the contact angles between several solid-liquid pairs at both macroscopic and microscopic scale. The solid substrates investigated include (001), (100) and (110) faces of quartz, and the test liquids are water, glycerol and phosphoric acid (85 wt%). The results obtained show that the solid-liquid contact angles, which were measured by optical goniometer and AFM, are nearly identical, indicating that both methods are reliable, although the optical goniometer measured the contact angle at macroscale and the AFM yielded results at nanoscale. For the three faces of quartz tested, the contact angles become greater in the order of (001), (110) and (100), although the change in contact angle of phosphoric acid is more obvious than those of water and glycerol. In order to explain the effect of the crystal faces on the contact angles, the molecular dynamic simulations were conducted to investigate the wetting characteristics of water droplets on (001), (100) and (110) faces of quartz. The simulation results demonstrate that the surface densities of unsaturated silicon atoms and the first-layer water molecules on the crystal faces are all in accordance with the order of (001) > (110) > (100), which is in the exact opposite order of the contact angles that were obtained in the experiments. Therefore, it can be inferred that the differences in the surface atomic arrangements and the surface density of unsaturated silicon atoms are the intrinsic causes of the wettability differences between quartz faces.
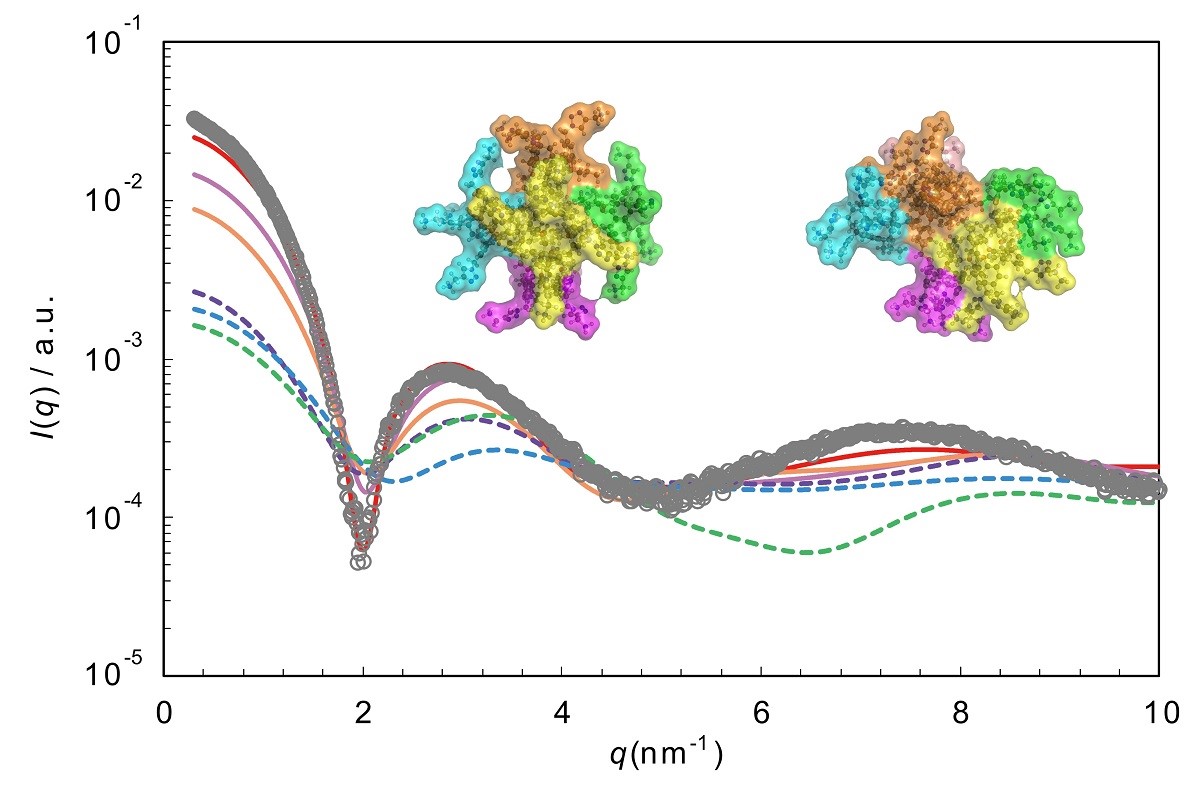
Supramolecules such as micelles are used as various functional materials. These functionality is dependent on the amount and/or type involved in the interaction of supermolecules, it is mainly expressed in the aqueous solution. Therefore, we have to understand the 3D structure of supramolecule in aqueous solution, and their information play important role to create a novel functional material. In our recent study, we reported about the analysis of calix[4]arene-based micelle by using various experimental methods. Calix[4]arene-based surfactants showed that they are monodisperse with a defined aggregation number whose values are chosen from the face number of Platonic solids. We named it “Platonic Micelle”. Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) provides nanoscale information about size and shape for disperse particle. However, it is difficult to understand a detail of the 3D configuration of the aggregate of the molecule forming the Platonic Micelle with only SAXS. Then, we considered that the 3D configuration of Platonic Micelle is able to understand by combination of the computational chemistry method and SAXS. The Platonic Micelle consisting calix[4]arene-based surfactant having four alkyl tails and four head groups were examined by SAXS and computational chemistry methods mainly using molecular dynamics (MD) simulation, molecular orbital method and CRYSOL program. CRYSOL program is able to provide a theoretical value about scattering. On the hands, a dynamics of Platonic Micelle can be analyzed with MD simulation. 3D configuration of Platonic Micelle was estimated by comparison between SAXS result and theoretical curve calculated in CRYSOL program by using 3D coordinates obtained in the process of MD simulation.
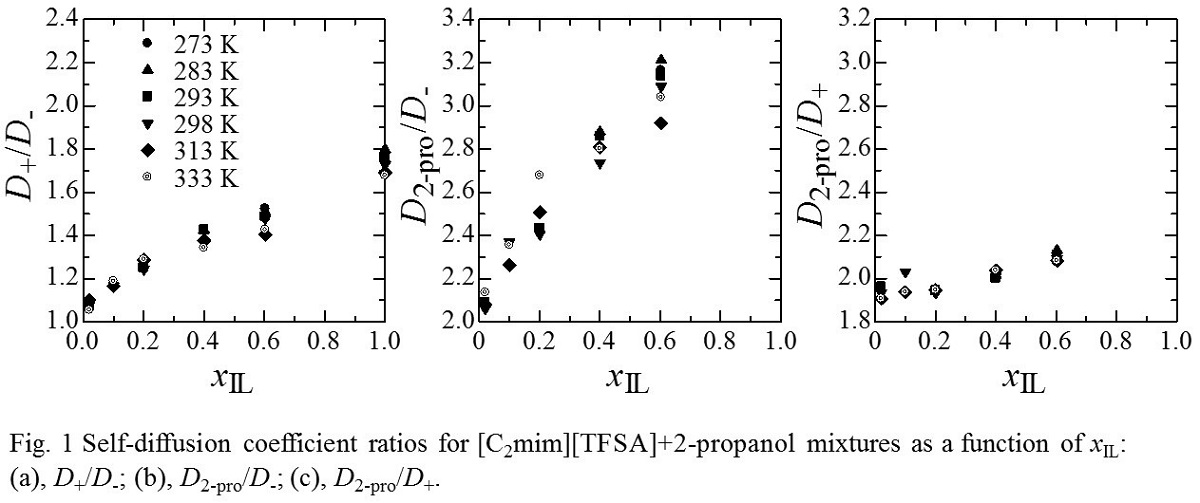
Several investigations have been reported on the phase behavior of ionic liquid (IL)+alcohol mixtures. For example, a 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolum bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide ([C2mim][TFSA])+2-propanol mixture shows upper critical solution behavior. The critical temperature and critical mole fraction (xIL) of IL for the [C2mim][TFSA]+2-propanol mixture are 292.2 K and xIL = 0.149, respectively. However, the transport properties of IL+2-propanol mixtures, such as viscosity, electrical conductivity, and self-diffusion coefficient, have not been investigated systematically.
In the present study, the self-diffusion coefficients of [C2mim]+ (D+), [TFSA]- (D-), and 2-propanol (D2-pro) for the [C2mim][TFSA]+2-propanol mixtures were measured using PFGSE NMR spectroscopy together with the density, viscosity, and electrical conductivity. In Fig. 1, D+/D-, D2-pro/D-, and D2-pro/D+ ratios for [C2mim][TFSA]+2-propanol mixtures at various temperature are plotted as a function of xIL. The D+/D- and D2-pro/D- ratios decrease with decreasing xIL, where the decrease in D2-pro/D- is more remarkable than D+/D-. On the other hand, the D2-pro/D+ ratio does not considerably change. Then, the increase in D- with decreasing xIL is significant compared with D+ and D2-pro. This is probably because [C2mim]+ interacts with 2-propanol more strongly than [TFSA]- in the mixtures. We will give the detailed discussion about intermolecular interactions in the [C2mim][TFSA]+2-propanol mixtures based on the results of the density, viscosity, and electrical conductivity measurements in the presentation.
In order to investigate the transport property of ionic liquids, we performed molecular dynamics (MD) simulation by using the non-polarizable force field developed with first-principles DFT calculations. The DFT calculations were implemented with the QUICKSTEP of CP2K[1]. The PBE-type generalized gradient approximation was employed for the exchange-correlation functional. Further information for the optimization scheme will be presented in the oral presentation. The cation is 1-alkyl-3-methyl-imidazolium, N-metyl-N-proylpyrrolidinium, and N-butyl-N,N,N-trimetylammonium. The counter anions are chloride, tetrafluoroborate, bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide, and bis(trifluorosulfonyl)amide. All the MD simulation were implemented by using Gromacs package[2]. Self-diffusion coefficients was evaluated with the Einstein equation and the modification of periodic boundary condition. Viscosity and electrical conductivity were evaluated with the Green-Kubo formulae. The calculated transport coefficients are in good agreements with the corresponding experimental data. Even for several systems based on the same cation or anion, since the molecular charges were updated via first-principles calculation at each thermodynamic states, the effective charges and van der Waals parameters were assigned for the MD simulation. Thereby, the MD simulation in the framework of the present molecular force field is useful to predict transport properties of various ionic liquids. In this poseter presentation, the calculated structural and transport properties will be discussed over the various compositions of ionic liquids including the ternary mixtures.
[1] CP2K, version 4.1, The CP2K Foundation, Zürich, 2014.
[2] Gromacs, version 2016.5, The GROMACS development teams, Sweden 2017.
Ionic liquids (ILs) generally have negligibly small vapor pressure and high thermal and chemical stability. They show higher solubilities of acidic gases such as CO2, H2S, NOx and SOx than neutral gases like N2, H2, and O2. The mixtures of diglyme (i.e. diethylene glycol dimethyl ether) and lithium salts show unique the physico-chemical behavior resembling ILs [1], therefore, they are called as “solvate ionic liquids (SILs)”. Since Aki et al. [2] reported that [TFSA]- is the best anion in the imidazolium salts for CO2 absorption, [Li-diglyme][TFSA] was expected to have the excellent CO2 absorption capacity. The CO2 solubility and calorimetric data are required for the development of the CO2 separation process using SILs.
In the present study, we have investigated the enthalpies of CO2 solution in diglyme and [Li-diglyme][TFSA] (LiTFSA: 10 wt%) at 313.2 K and up to 7.0 MPa using a flow calorimetric technique. The experimental values of the enthalpies were consistent with the calculated ones based on the Henry's constants [3]. Furthermore, the CO2 solubilities were derived from the experimental calorimetric data for diglyme and [Li-diglyme][TFSA]. The CO2 solubilities determined by the present calorimetric approach agreed fairly well with the synthetic approach [4].
References
[1] K. Ueno et al., J. Phys. Chem. B, 116, 11323-11331 (2012)
[2] S.N.V.K. Aki et al., J. Phys. Chem. B, 108, 20355-20365 (2004)
[3] D. Almantariotis et al., Int. J. Greenh. Gas Con., 10, 329-340 (2012)
[4] D. Kodama et al., Fluid Phase Equilib., 302, 103-108 (2011)
Polymers have been widely used for controlled release materials in various fields such as fragrances and medicines. In this work, we have focused on copolymers as controlled release carriers with respect to their controllability of solubility and diffusivity of released solutes by changing copolymer composition as well as by tuning operation conditions. Regarding a solute, CO2 was selected by considering its potential antioxidant effect. We have conducted measurement and correlation the solubility and diffusivity of CO2 in poly (methyl methacrylate (PMMA)) and poly (methyl methacrylate (MMA) / ethyl acrylate (EA)) copolymer. This copolymer shows glass transition temperature, Tg, at 70–130 °C depending on EA content. In addition, Tg is reduced to near room temperature by CO2 dissolution, of which feature is very useful for controlled release design since solubility and diffusivity change drastically around glass transition. The measurement conditions were the temperatures of 10, 25 and 40 °C close to supposed practical conditions of the controlled release material. The measurement results of the CO2 solubility in PMMA increased with increasing pressure, and decreased with increasing temperature. These results indicated that the dissolution of CO2 in this copolymer could be governed by the condensability of CO2. In addition, it would be noted that the CO2 solubility data were correlated fairly well with the Dual-Mode-Sorption [1] in conjunction with the SL-EOS [2, 3].
Now measurements of Tg of this copolymer under high pressure CO2 are on-going with aiming the improvement of solubility/diffusivity correlation near glass transition by introducing Tg value to the correlation model.
References:
[1] N. H. Wang, et al., Kagaku Kougaku Ronbunshu, 2, 226 (1996).
[2] I. C. Sanchez and R. H. Lacombe, J. Phys. Chem., 80, 2352 (1976).
[3] I. C. Sanchez and R. H. Lacombe, Macromolecules, 11, 1145 (1978).
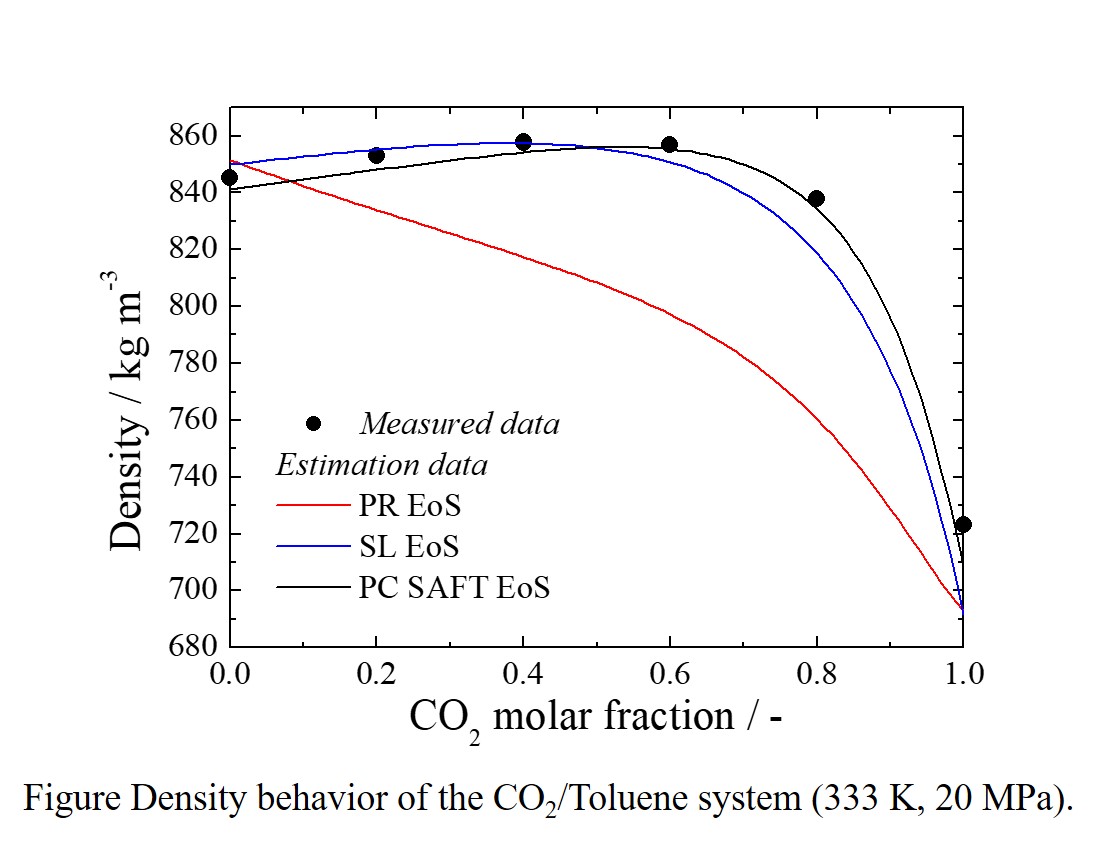
Recently, attention has been focused on a mixed fluid in which carbon dioxide (CO2) is dissolved in an organic solvent, a so-called CO2 expansion liquid. Since this mixed fluid can widely change the solvent characteristics only by pressure operation, its application as extraction of natural products and generation of fine particles has been studied. The equilibrium and/or transport properties such as density, dielectric constant, and viscosity of the mixture change greatly depending on the composition of CO2. So, for industrial process design, it is important to grasp the physical properties of the CO2 and organic solvent mixture. However, the measured data is insufficient at present because physical property measurements under high pressures need a special device and a long time. Therefore, the estimation of physical properties is greatly needed. In this study, the density of uniform fluid mixture under high pressure was focused on, which is the property greatly affected by composition. The density of CO2 and toluene uniform fluid mixture was measured, and the applicability of the three mainstream equations of state to density estimation was evaluated. The density of CO2 and toluene uniform fluid mixture was measured with a high pressure vibration type density meter equipped with a circulation pump and a variable volume viewing cell. The calibration of the density meter was conducted with water and cyclohexane. The measurement was conducted at temperatures from 313.2 K to 353.2 K and pressures up to 20 MPa. CO2 compositions were changed from 0 (pure toluene) to 80 mol%. In density estimation, the Peng-Robinson equation of state as a representative of the van der Waals types, the Sanchez-Lacombe equation of state as a representative of the lattice fluid theory types, and the PC SAFT equation of state as a representative of the statistical associating fluid theory types were used.
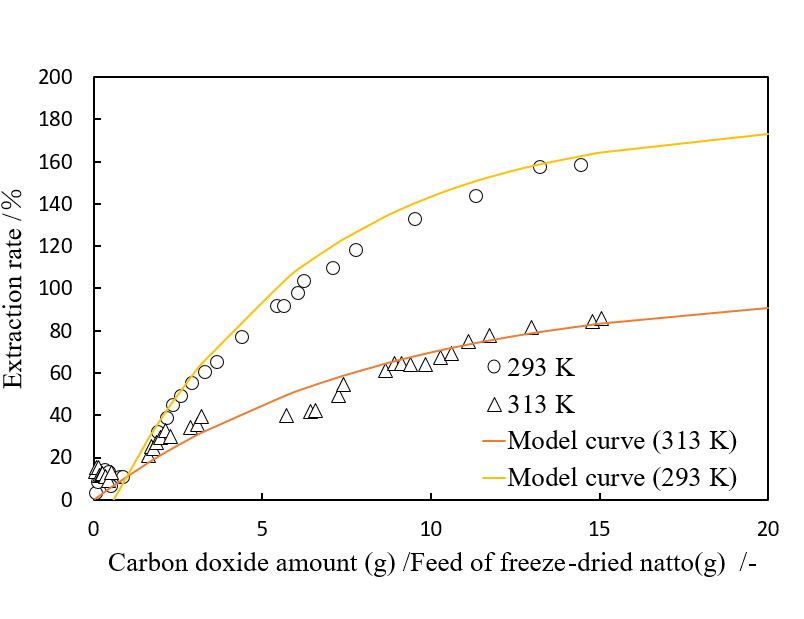
Vitamin K is essential for osteogenesis, and vitamin K deficiency causes osteoporosis leading to hip fracture and coronary disease. Menaquinone-7 (MK-7), one of vitamin K subtypes, is abundantly contained in Japanese traditional fermented food natto. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of freeze-dried natto was investigated at 293 K and 313 K at 100 atm, by means of semi-batch flow-type equipments. The extraction rate of the oil from freeze-dried natto was defined as a ratio of the extraction yield to a traditional hexane extraction yield. To improve an oil recovery during the extraction, the collection trap was cooled with brine bath. The extraction yield at lower temperature condition was improved due to an increase of oil solubility. The maximum yield of extracted oil was 158.4% at 293 K and 10 MPa. The qualitative analysis for the extracted oil by UPLC/Q-Tof was performed to identify elemental composition of valuable compounds. The elemental composition analysis was revealed that that the menaquinone-1, 2, 3, isoflavone, and linoleic acid were identified by comparing monoisotopic masses between theoretical and measured values. The time profile of the extraction rate was indicated that the amount of extraction oil increased with the cosumption of carbon dioxide. The time profiles of extraction rate were fitted by simple mathematical model. The time constants of the mathematical model were 0.15 at 293 K and 0.12 at 313 K. The time profile of the mathematical model is comparable with that of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. The maximum extraction rate would be 180% at 293 K with 23 g/g of carbon dioxide.
A mixture fluid of CO2 and an organic solvent is expected as a new reaction solvent [1] because its properties can be varied by changing pressure, temperature and/or composition. To use the mixture fluid for industry, fundamental property data in wide pressure and entire composition range are needed. However, reports on diffusion coefficients D1m in mixtures of CO2 and organic solvent are limited [1]. Furthermore, high accurate prediction models for D1m in mixture fluids are not well established. In this research, D1m's of phenol in a mixture fluid of CO2 and methanol under high pressure conditions were measured by the Taylor dispersion method. Moreover, the D1m data measured experimentally were compared to D1m values calculated by the Blanc's equation [1]. Each fluid (CO2 and methanol) was separately supplied by each syringe pump at a constant flow rate to the diffusion column. A methanol solution of phenol was loaded via the injector to the diffusion column. A response signal was obtained at the exit of the diffusion column with a UV-Vis photodiode-array detector. The D1m and velocity u were simultaneously determined such that fitting error, ε, defined by eq. (3), was minimized by changing D1m and u values. D1m decreased with increasing methanol molar fraction because fluid viscosity increased as methanol molar fraction increased. D1m's were predicted by the Blanc's equation defined by eq. (4). The prediction performance for all the data points was lower than 11% in relative deviation Herein, m is the amount injected, R and L are the radius and length of diffusion column, respectively, t is the time, and exp and cal designate experimental and calculation, respectively. x is the molar fraction, and D1A is the binary diffusion coefficient for phenol in A solvent.
[1] T. Funazukuri et al., Fluid Phase Equilib., 164, 117 (1999).
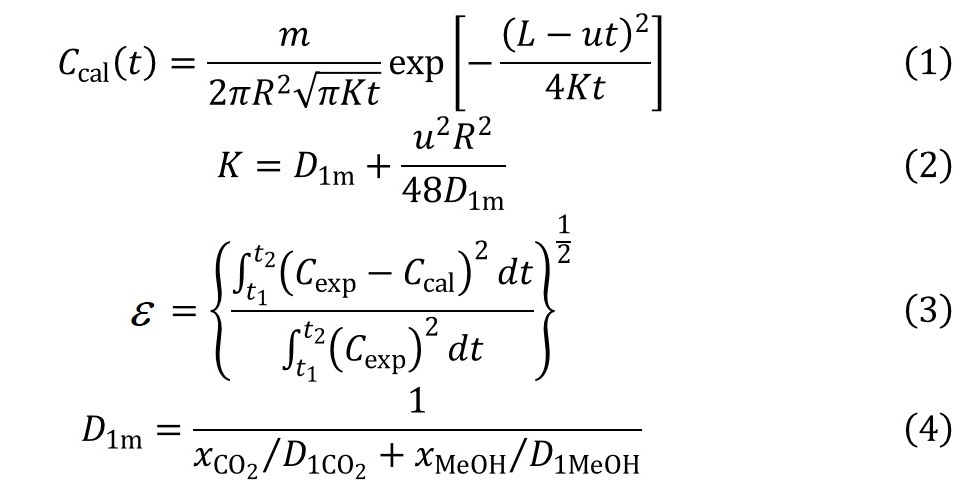
We mainly focus on the cocrystal formation of poorly soluble drug with CO2, targeting on the enhancement of drug solubility and improvement of drug dissolve behavior. In this work, norfloxacin was used as target drug, which have a very limited solubility about 0.28mg/g water at 25 °C. To form the cocrystal of Norfloxacin with CO2, we treat put Norfloxacin anhydrate in hyper-pressure cell in a temperature-controlled (30 to 60 °C) thermostatic oven and pressurize the CO2 into the cell until determined pressure (5 to 25MPa) is reached. Then the pressure and temperature are controlled as a constant for 2h. After this, the hyper-pressure cell is depressurized at 0.1MPa/min. And the solid (mixture of Norfloxacin and Norfloxacin CO2 cocrystal) remained in hyper-pressure is collected, we call it Norfloxacin Sc-CO2. After the experiment, the Norfloxacin Sc-CO2 is characterized mainly by powder XRD for semi-quantification of new formed cocrystal, and solubility test to check the dissolve behavior change. As results, we find out the higher pressure and higher temperature are preferred for cocrystal formation. Moreover, as can be seen in Figure, more cocrystal is formed, higher solubility of Norfloxacin we can get. In this research, the highest solubility is achieved at 25MPa, 40 °C, 0.64mg/g water at 25 °C, about 2 times higher than raw Norfloxacin. We also use the FT-IR to characterize the chemical change before and after Sc-CO2 treatment, and find two new peaks at 1650 cm-1 which may indicate the C=O vibration of CO2, and 990cm-1 which is still unknown. And TGA test give a mass loss around 189 °C corresponding with new heat absorbance in DSC test, which suggest the release of CO2 from the cocrystal.
Supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) is considered as a green and environmental friendly solvent. scCO2 has been widely used for dyeing for textile and polymer processing. In the design and development of scCO2 process, solubility is one of the important and fundamental property. So far there are many calculation models developed for fitting and prediction of the solubility of dyestuffs. For example, Chrastil, Mendez-Santiago – Teja, Bartle et al., Kumar – Johnston, Garlpati – Madra, Sung – Shim, Adachi – Lu, and Ch – Madras proposed scCO2 density-based models to correlate the solubilities of solid compounds. Also the equations of state like Peng – Robinson and Soave – Redlich – Kwong were used to fit and predict solubility of solid compounds in scCO2. Recently the solubility calculation was performed by the equation of state combined with gE model. In these calculations of fitting and prediction of the solubility, we encountered some inconveniences in an accurate representation of the models to the whole range of the experimental results and in dependence of the functional flexibility for the model used. To overcome these shortcomings, the neural network was applied to represent the solubility. In the present work, we examined to correlate and predict accurately the solubility of anthraquinone and the derivatives in scCO2 by the neural network.
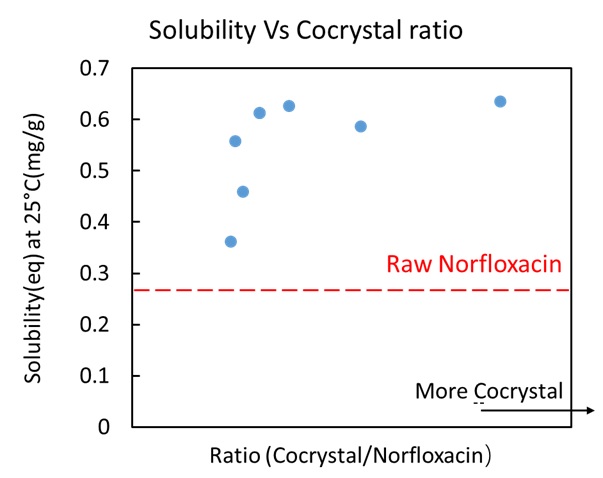
Recently, VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) emission to environment has become a serious problem. In particular, the paint industry is the largest VOC emission source in Japan, because large amounts of VOC are used as diluents in paint. As a new alternative technology, a CO2 painting system [1], which replaces a part of solvent (diluent) with high pressure CO2, has attracted an attention, because it can reduce VOC emission and drying cost. The fluidity of paint is important in the painting process, however viscosity data of CO2 + organic solvent + polymer system are rarely reported. In this work, viscosity, density, and bubble-point pressure of CO2 + methanol system were measured at 40 and 80 °C. To ensure the measurements at one phase, our pressure conditions were set at 0.2 MPa higher than the saturation. Figure shows experimental viscosity data of CO2 + methanol system at 40 °C. Viscosity tends to decrease with increasing CO2 composition and increase with increasing pressures. Estimated saturated viscosity data of this work were smaller than that of Sih et al. [2], and the deviation were 4.5 ~ 8.9 %. However, viscosity data at 0.1 MPa in pure methanol which were obtained by extrapolation from experimental data were in good agreement with the reliable literature values [3]. Free Volume Theory proposed by Allal et al. [4] was applied for the viscosity correlation and prediction. The predicted results of CO2 + methanol viscosity at 40 °C could well represent the experimental data.
References:
[1] S. Kawasaki et al., J. Jpa. Soc. Colour Mater., 86, 163 (2013).
[2] R. Sih et al., J. Supercrit. Fluids, 41, 148 (2007).
[3] H. W. Xiang et al., J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 35, 1597 (2006).
[4] A. Allal et al., Phys. Rev. E, 64, 011203 (2001).
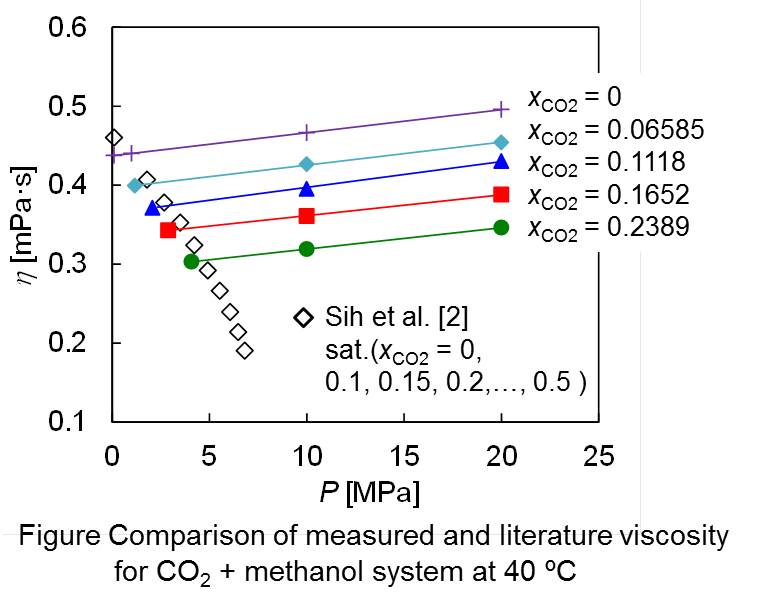
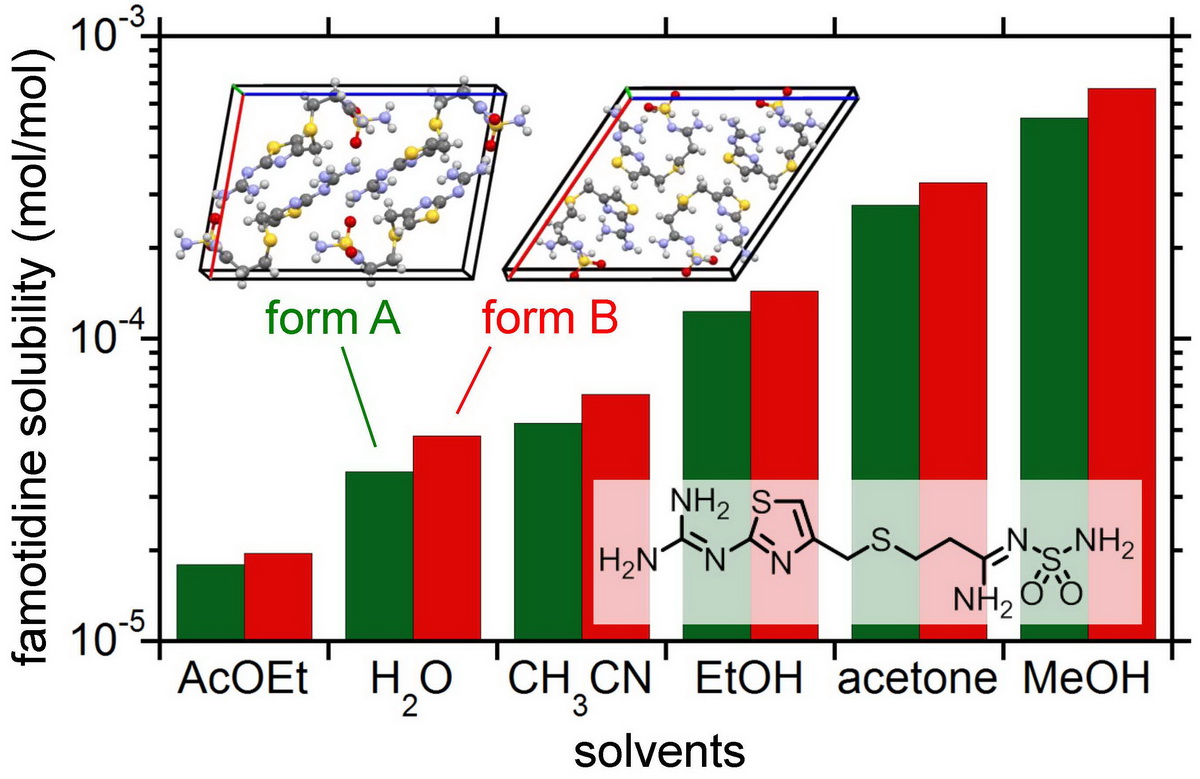
Most pharmaceutical drugs have several crystal polymorphs, i.e., solid phases with different crystal structures. The polymorphs have different properties with each other, such as the solubility, stability, and particle shape, therefore affecting the bioavailability and the separation efficiency. It is thus required in pharmaceutical industry to selectively crystalize a target polymorph with desirable property. Solubility data of the polymorphs are essential information for the selective crystallization. Here we measured the solubility of famotidine, a histamine H2 receptor antagonist, in various solvents at 298.15 K. Famotidine has the two polymorphs, a stable form A and a metastable form B. For both polymorphs, the solubility increased in the order of ethyl acetate < water < acetonitrile < ethanol < acetone < methanol. In all the solvents, the solubility of form B was larger than that of form A. The solubility ratio B/A varied with the solvent from 1.09 to 1.32 in the order of ethyl acetate < ethanol < acetone < acetonitrile < methanol < water. The experimental solubility ratio was smaller than that estimated (1.48) from the melting temperature and the molar enthalpy of fusion for the polymorphs. The solvent effects on the polymorphic solubilities and the solubility ratio are discussed in comparison with those for other pharmaceutical drugs.
Kinematic viscosity is one of the important transport properties, and is required for designing chemical process as well as estimating transport parameters via dimensionless numbers such as Reynolds number, Schmidt number, Prandtl number etc. [1]. In some models for calculating kinematic viscosities, some excess free energy models based on the local composition idea with Eyring equation will be useful from a practical of point.
This paper reviews the models for calculating kinematic viscosity using modified Eyring and excess free energy models.
1. Kinematic viscosity at normal pressure
1.a. Correlation of kinematic viscosity for binary system [2]
1.b. Prediction of kinematic viscosity for multi-component system [2]
1.c. Prediction of kinematic viscosity using ASOG-VISCO [3]
2. Kinematic viscosity at high pressure
2.a. Prediction of high-Pressure viscosity from viscosity data at normal pressure [4]
2.b. Prediction of kinematic viscosity at high-pressure using ASOG-VISCO [5]
References
1) B.E. Poling, J.M. Prausnitz, J.P. O'Connell: The Properties of Gases and Liquids, 5th ed., McGraw-Hill, New-York (2001)
2) H. Matsuda, K. Tochigi, K. Kurihara, T. Funazukuri, V. K, Rattan: accepted for Fluid Phase Equilibria
3) K. Tochigi, K. Yoshino, V. K. Rattan: Int. J. Thermophysics, 26, 413-419 (2005)
4) K. Tochigi, T. Okamura, V. K. Rattan: Fluid Phase Equilibria, 257, 228-232 (2007)
5) H. Matsuda, K. Kurihara, K. Tochigi, T. Funazukuri, V. K. Rattan: Fluid Phase Equilibria, 470, 188-192 (2018)
Solid–liquid equilibria (SLE) for three binary mixtures of Dodecanoic acid with n-octadecane, n-eicosane, and n-docosane were measured using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC).Simple eutectic behaviors for all three systems were observed. The eutectic point of the (Dodecanoic acid + n-octadecane) system is at 300.15 K and 0.302 mole fraction of Dodecanoic acid, that of the (Dodecanoic acid + n-eicosane) system at 306.60K and 0.558 mole fraction of Dodecanoic acid and that of the (Dodecanoic acid + n-docosane) system at 311.15 K and 0.661 mole fraction of Dodecanoic acid.
Dimethyl ether (DME) and propane are easily liquefied because they have relatively low vapor pressure among liquefied gases and used for aerosol propellant. A new solvent has been proposed to synthesize nanoparticle by using the mixture of liquefied propellant and alcohol. Therefore, the polarity and the volatility can be controlled by the composition of the solvent. In our research group, the dielectric properties has been already measured for liquefied DME + ethanol and liquefied propane + ethanol mixture. In this study, the complex dielectric spectra of liquefied DME + propanol (1-propanol and 2-propanol) and propane + propanol (1-propanol and 2-propanol) mixture were measured at 303.2 K. The complex dielectric spectra of DME + 1-propanol and DME + 2-propanol liquid mixture were measured by frequency domain method with the network analyzer (HP8720C). Coaxial probe was used for the dielectric spectra measurement in the frequency range of 0.5 ~ 18 GHz. Frequency dependence of the complex dielectric spectra was fitted by single-phase Debye equation, and the static dielectric constants and the dielectric relaxation times of DME + propanol and propane + propanol liquid mixture at 303.2 K were determined. The static dielectric constants of all mixtures studied decreased with increasing liquefied gas concentration. The dielectric relaxation times of DME + propanol liquid mixture decreased with increasing DME concentration. For propane + propanol liquid mixtures, however, the propane composition dependence of dielectric relaxation time show maximum. The excess dielectric constants and the excess inverse relaxation times were calculated from the static dielectric constants and dielectric relaxation time studied. These excess values disclose the hydrophobic interaction between liquefied gas and alkyl chain of propanol plays important role of the liquefied gas dependence of dielectric properties for all mixtures studied at 303.2 K.
As a part of the development of the Hydrogen Organic Career, Hydrogen+Methyl-cyclohexane (MCH) system VLE model is developed for evaluation of MCH production process. Thermodynamic model using Peng-Robinson Equation of state which modified by Boston, Mathias is correlated using VLE data by Tsuji (2005) and Peter(1960). The conceptual MCH synthesis process is modeled using Aspen plus to evaluate the process performance and energy consumption.
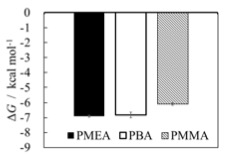
The performance of polymer as biocompatible or separation material can be governed by its ability of adsorbing biological molecules. Considerable efforts have been devoted to characterize the polymer/water interface with the purpose of predicting the adsorption tendency, while the adsorption free energy is the direct measure of the extent of adsorption of an adsorbate of interest. In this study, the adsorption free energy was calculated by extending the energy-representation method to the polymer/water interface. We focused on the adsorption of amino-acid analogs onto poly(2-methoxyetyl acrylate) (PMEA), poly(butyl acrylate) (PBA), and poly(methoxyetyl acrylate) (PMMA). The MD simulation of the polymer/water systems was performed with GROMACS 5.1.4 in the NPT ensemble at a temperature of 300 K. The TIP3P model was used for water, and the polymer and amino-acid analog were described by potential functions that are based on the general AMBER force field (GAFF). The free energy of adsorption on the polymer/water interface was computed by the energy-representation method by viewing the polymer and water as a mixed solvent with a restraint on the adsorption depth. p-Cresol is one of the amino-acid analogs examined, and Figure shows its adsorption free energy ΔG onto each polymer at the Gibbs dividing surface. ΔG is favorable (negative) and p-cresol binds favorably to the polymers examined. The equilibrium content of water is larger in PMEA than in PBA and PMMA, while ΔG is in the order of PMEA ≈ PBA < PMMA. Thus, the adsorption free energy does not necessarily correlate with the interaction of polymer with water.
In recent years, Blood viscosity considered to be important from the viewpoint of prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases in a medical field. Measurement of blood viscosity is difficult due to its coagulation property and measurement method of blood viscosity has not been established yet. We developed a compact sized Falling Needle Rheometer which is able to measure the blood viscosity almost immediately after collection. A Falling Needle Rheometer can measure the viscosity of a liquid with high accuracy ±0.1% in a short time and a viscosity measuring method is simple and anyone can get highly precise data easily. The blood is withdrawn from the body flowing into vacuumed plastic tubes coated with an anticoagulant. On the other hands, blood was withdrawn with non-Coated with anticoagulant vacutainer tubes and measured within 30 seconds. The blood always remained inside the vacutainer vessel and the viscosity was measured via a falling needle with a distinctive mass. We observed the effect of human blood viscosity on the addition of anticoagulants. We chose EDTA and heparin as anticoagulants. As a result, the human blood with anticoagulant shows higher viscosity than that without anticoagulant. We succeeded in measuring the flow characteristics of human blood using Falling Needle Rheometer.
The Hansen solubility parameter (HSP) is one of the index for affinity of materials with some solvents. The basic principle of HSP has been ‘like dissolves like'. HSP values over 1200 kinds of pure solvents have been reported by Hansen in the data base of HSPiP program 2004. Furthermore, HSP value is used for various research fields, such as an evaluation of the solubility of solid in solvent, a compatibility and an affinity of polymers in solvent and a dispersibility of fine particles in solvent. The other side, one of the methods of HSP for a liquid or its mixture is able to measure from physical properties of the solvent (such as refractive index, surface tension, permittivity and dipole moment). In the case of solvent mixture, the non-ideality of the solution is so important for practical use, however, non-ideality of Hansen solubility parameter for solvent mixture has not been elucidated so far. In this research, the comparison between the HSP value calculated from the physical properties (δt is calculated from surface tension, δd is refractive index, δp is permittivity, δh is calculated from solvent polarity parameter) and the HSP value calculated from the volume fraction ideal was carried out, and the non-ideality of solvent mixture were discussed and confirmed. In addition, this non-ideality created the estimation equation by the activity coefficient used in creating the estimation equation of the mixture.
Ethanol has been widely used in our daily life as a solvent for deodorizer, medicine, cosmetics and pesticide because of its bacterial killing and human friendly natures. The knowledge of miscibility and solubility with some propellants is important for designing their spray cans. In this study, bubble point pressure of the three binaries, containing ethanol with conventional or new propellant, were measured by use of a static apparatus at the three isotherms, 293.15, 303.15 and 313.15 K. The propellants employed were two conventional ones, propane and dimethyl ether, and new one, (E)-1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene (HFO-1234ze(E)). These are expected as alternatives of CFC-12 and HFC-134a. The glass cell, with the inner volume of 37 cm3, was equipped in the apparatus, and the detail equipment has been reported elsewhere. The experimental temperature was measured by a thermistor thermometer with the estimated uncertainty, u(T)=0.04 K. The pressure was by the three pressure sensors with the different maximum capacities, 10 MPa(gauge), 1MPa(gauge) and 200kPa (abs.). The estimated uncertainty is u(P)=0.5 kPa for P > 100 kPa, and u(P)=0.06 kPa for P<100 kPa, respectively The three binaries showed the non-ideality in the solution, and the positive deviations from Roult law was observed in the whole range of the experimental temperature. The non-ideality in propane + ethanol and HFO-1234ze(E) + ethanol seemed to be larger than that in dimethyl ether + ethanol. The bubble pointy pressure was correlated with non-random two liquid (NRTL) model. The calculation showed good reproducibility Then.the average absolute relative deviations were 0.70, 0.62 and 1.68 % for ethanol with propane, dimethyl ether and HFO-1234ze(E), respectively.
FLiBe(2LiF-BeF2)molten salts are expected to serve as the coolant and the thorium-uranium fuel dissolver in molten salt reactors, with the advantage of low pressure operation, good stability under radiation, high solubility of uranium and thorium fuel, and low corrosion to structural materials. In order to purify and obtain the high quality salts, a mixture of H2 and HF is used to remove oxygen impurity from FLiBe molten salts.
In this study, Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics simulations with BLYP method were performed to investigate the structure, transport properties of H2, HF diffusion through liquid FLiBe(2LiF-BeF2) in the range of 773–973K. Radius distribution functions and first-shell coordination numbers of the molten salt obtained by Ab initio molecular dynamics calculations reproduce the data of experimental measurement. The structure of the melts reveals the existence of a network of BeF42-, Be2F73-,Be3F104-. The self-diffusion coefficients extracted from mean square displacements of F-, Li+ and Be2+ are in accord with values found in literatures. The diffusion coefficients of H2 and HF were obtained within error allowed. The results show that the diffusion coefficient of HF is a little higher than that of F- ion, because the F- in HF molecular easily stays bonded to Be2+ like other F- while the H+ of HF moves quickly.
Through the work, the diffusion coefficient of HF was obtained to calculate the basic data of gas-liquid mass transfer, and provide basis for reactor design and scale up the FLiBe purification process.
Nanoparticle Organic Hybrid Material (NOHM) is a new green platform material which is self–suspended liquid–like material consisted of inorganic core and organic canopy. This new platform, NOHM, has been evaluated to have high potential for various energy and environmental applications such as CO2 sorptive materials, electrolytes, and lubricants with a low vapor pressure and promising thermal stability at high temperature over 200 °C. More importantly, NOHM has a great tunability on both entropic and enthalpic designs by introducing tailored core and linkage with specific functionalities. In particular, the entropic property which related to the intramolecular interactions between core and canopy structure could influence on the system's thermal, chemical, and electrical properties. In this investigation, it was designed to evaluate the entropic packing effects of NOHM systems on thermal properties and swelling behavior. The four different NOHM systems with varying the core size and the suspension system were synthesized (single 7, 12, 22 nm suspension and ternary suspension) and their thermal properties and swelling patterns were investigated via thermal analysis and spectroscopic analyses including ATR FT-IR and DOSY NMR. Through the investigation, the entropic packing effects by core size were identified. In addition, the ternary suspended NOHM system were evaluated to have high potential for thermal fluid application.
In this paper, a machine learning method is proposed to extract molecular features as floating-point numbers in a high dimensional space by mapping a language-like description Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry Specification (SMILES) to a molecular fingerprint known as Molecular ACCess System (MACCS) which represent the molecular features as an one-dimensional array of molecular features. Two neural network models are build to predict the “sigma-profile”, the charge distribution of the molecule near a perfect infinite conductor, which is calculated by quantum mechanics. The sigma-profile can be used in the COSMO-SAC model for predicting thermodynamic properties such as activity coefficient. One uses MACCS as direct input, and the other uses the high dimensional space representation as input. Preliminary results showed that an accurate neural work model that uses the high dimensional space representation is much better than the one using MACCS. The results indicate that projection of molecular features into a high dimensional space with spatial features and distance metric is a much better representation of molecular features and potentially be a better predictor of thermodynamic properties.
Dry reforming of methane (DRM) is important in the reduction of greenhouse gases and their conversions to useful products. Substituted metal catalysts have emerged as a new category of oxide catalysts making an intensive impact on environmental catalysis. Density functional theory (DFT) is the powerful technique for finding the active nature of new catalytic material. Hence, in this study, we have extensively used DFT calculations to design and probe a novel DRM catalyst. We selected Ru and La2O3 due to their hindered nature towards carbon formation making it a potentially non-deactivating catalyst. Vacancy formation energy decreased on Ru substitution when compared to that observed with La2O3, thereby improving the reducibility of the substituted catalytic material. Carbonates play a crucial role in DRM reaction on basic supports and hence, so we probed different types of carbonates present over Ru-substituted La2O3. Our theoretical calculations were successfully verified with experiments. Reducibility of Ru-substituted La2O3 was probed using temperature programmed reduction profiles (TPR). DRIFTS was carried out to determine the importance of carbonates during DRM reaction. Both theoretical and experimental studies proved Ru-substituted La2O3 a good catalytic material for DRM reaction.